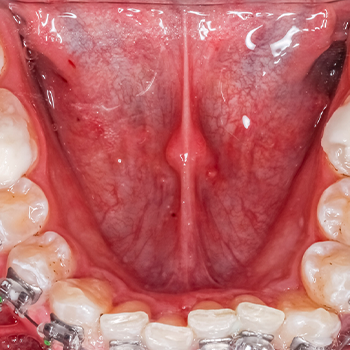
Denture stomatitis, also known as Candida-associated denture-induced stomatitis (CADIS), is a common fungal infection that affects individuals who wear dentures. This condition primarily involves inflammation of the oral mucosa beneath a denture, often resulting from the accumulation of Candida albicans, a type of yeast. However, when the balance of microorganisms in the mouth is disrupted, Candida can overgrow, leading to infection and inflammation.
Who suffers from Denture Stomatitis?
Denture stomatitis is prevalent among individuals who wear removable dentures, both full and partial. While it can affect people of all ages, it is more commonly observed in older adults. This may be attributed to factors such as reduced saliva production, changes in oral flora, and compromised immune function that often accompany aging. Additionally, individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, may be at an increased risk of developing denture stomatitis.
Causes and Symptoms of Denture Stomatitis
Causes
Denture stomatitis is primarily caused by the overgrowth of Candida albicans, a naturally occurring yeast in the oral cavity. Several factors contribute to the development of this condition, including poor oral hygiene, ill-fitting dentures, inadequate denture cleaning, and prolonged denture use without proper removal.
Symptoms
The symptoms of denture stomatitis can vary in severity, and some individuals may not experience noticeable symptoms. Common signs include:
- Redness and inflammation of the oral mucosa beneath the denture.
- Discomfort or soreness in the affected area.
- Burning sensation.
- Development of red or white patches on the palate or other areas covered by the denture.
How is it Diagnosed?
Diagnosing denture stomatitis typically involves a comprehensive examination by a dentist or oral health professional. The healthcare provider will review the patient's medical history, inquire about symptoms, and conduct a thorough oral examination. In some cases, a swab or scraping of the affected area may be taken to identify the presence of Candida albicans or other microorganisms.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment
The management of denture stomatitis generally involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, proper oral hygiene practices, and antifungal treatment. Treatment options include:
-
Antifungal Medications:
Topical or systemic antifungal medications, such as nystatin or fluconazole, may be prescribed to eliminate the Candida infection.
-
Denture Care:
Ensuring proper denture hygiene is crucial. Dentures should be removed and cleaned thoroughly each night. Soaking dentures in an antifungal solution can also help eliminate Candida.
-
Oral Hygiene:
Maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing the gums, palate, and tongue regularly, even when dentures are removed, can prevent the recurrence of infection.
-
Prevention:
Taking preventive measures is key to avoiding the development of denture stomatitis. Here are some tips:
-
Proper Denture Fit:
Ensure that dentures fit well and are regularly assessed by a dentist for adjustments.
-
Good oral Hygiene:
Practice regular oral hygiene, including cleaning the gums, tongue, and palate. This helps maintain a healthy balance of oral flora.
-
Regular Dentist Visits:
Schedule routine dental check-ups to monitor oral health and address any issues promptly.
-
Healthy lifestyle:
Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and adequate hydration, to support overall immune function.
FAQ:
What mouthwash is best for denture stomatitis?
Antifungal agents can be used as an adjunct to these local measures, particularly to reduce palatal inflammation before taking impressions for new dentures. Chlorhexidine mouthwash is also effective against fungal infections.
What is the fastest way to cure stomatitis?
Your body has no way of getting rid of the virus. However, the outbreaks aren't severe, so this stomatitis can be managed with over-the-counter medications for pain relief and fever reduction. Children should also consume plenty of liquids during an outbreak. Outbreaks usually last two weeks or less.
What vitamin deficiency causes stomatitis?
Recurrent aphthous stomatitis can also result from a nutritional deficiency, particularly lack of iron, vitamin B3 (as in pellagra), vitamin C (as in scurvy), folic acid, or vitamin B12.